以下の記事で、2次元空間での最小二乗法について書きましたが、今回はそれをn次元空間に拡張してみます。
目次
三次元空間でのL2ノルム最小化
三次元空間までは可視化できるので、Pythonの以下のモジュールを使って三次元空間について考えていきます。
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from numpy.linalg import solve三次元空間上において、
$$\hat{f} (x,y) = c_1x + c_2 y + c_3,\:\: \forall c_n \in \mathbb{R}$$
とします。
これを行列表示すると、以下のようになります。
$\begin {pmatrix}x_1&y_1&1\\\vdots&\vdots&\vdots\\x_i&y_i&1\end{pmatrix} \begin {pmatrix}c_1\\c_2\\c_3\end{pmatrix} =\begin {pmatrix}f(x_1,y_1)\\\vdots\\f(x_i,y_i)\end{pmatrix} $
よって、
$A\mathbf{x} = \mathbf{b}$
と書くことができます。
この$\mathbf{b}$をAの像($ImA$)に射影することで、L2ノルム最小解を得ることができます。
Pythonで実装
x = [i-1 for i in range(100)]
y = [3*i + x[i] for i in range(100)]
z = np.array([2*i*random.random()-10*j*random.random() for i,j in zip(x,y)])
A = np.array([[float(i),float(j),float(1)] for i,j in zip(x,y)])
A_t = np.transpose(A)
b = np.transpose(z)
left = A_t@A
right = A_t@b
d = solve(left,right)
z_hat = [i*d[0]+j*d[1]+d[2] for i,j in zip(x,y)]
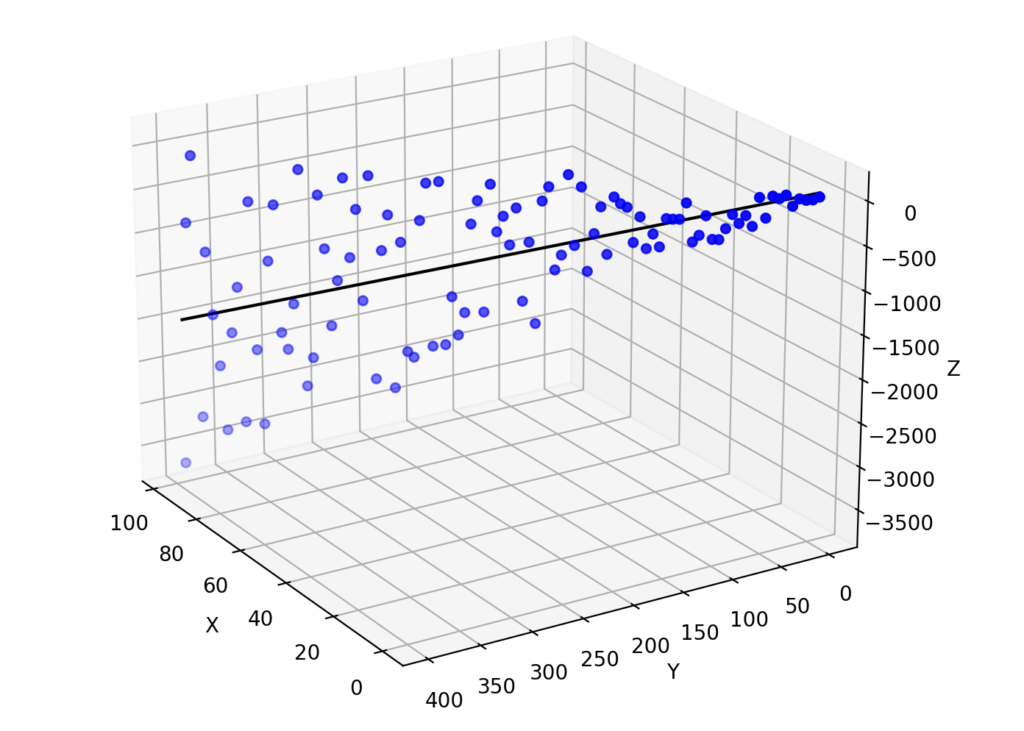
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111,projection='3d')
ax.scatter(x, y, z, color='blue')
ax.plot(x,y,z_hat,color = "black")
ax.set_ylabel("Y")
ax.set_xlabel("X")
ax.set_zlabel("Z")
ax.view_init(elev=10, azim=100)
fig.savefig("sd.png",dpi = 300)
plt.show()
>>>
[ 38.81344475 -14.1410778 -4.30833333]実行結果
n次元空間に一般化
n次元空間において、
$\hat{f} (w_1\dots w_n) =c_n +\sum_{i=1}^{n-1} c_iw_i,\:\: \forall c_i \in \mathbb{R}$
とします。
行列表示に変換すると、
$\left( \begin{array}{ccc} w_{11} & \cdots & w_{n 1}&1 \\ \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\ w_{1 i} & \cdots & w_{n I}&1 \end{array}\right)\begin {pmatrix}c_1\\\vdots\\c_i\end{pmatrix} = \begin {pmatrix}\hat{f}_1\\\vdots\\\hat{f}_i\end{pmatrix} $
よって、
$ \textbf{W}\mathbf{c} = \mathbf{F} $
を得ます。
2,3次元の時と同様に変形すると、
$\mathbf{c} = (\textbf{W} \textbf{W}^\mathrm{T})^{-1} \textbf{W}^\mathrm{T}\mathbf{F}$
この式について、4次元の場合をpythonで実装してみます。
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from numpy.linalg import solve
n = 100
v_1 = [np.random.randint(110,1000)/10 for i in range(n)]
v_2 = [v_1[i]+ np.random.randint(110,1000) for i in range(n)]
v_3 = [np.random.randint(110,1000) +10 for i in range(n)]
v_4 = [i+j+k + np.random.randint(110,1000) for i,j,k in zip(v_1,v_2,v_3)]
print(v_4)
A = np.array([[float(i),float(j),float(k),float(1)] for i,j,k in zip(v_1,v_2,v_3)])
A_t = np.transpose(A)
f = np.transpose(v_4)
left = A_t@A
right = A_t@f
d = solve(left,right)
z_hat = [i*d[0]+j*d[1]+k*d[2]+d[3] for i,j,k in zip(v_1,v_2,v_3)]
print(d)
>>>
[ 1.80955508 0.99178021 0.99809743 463.05190159]